Formidable Info About Can You Run 3 Phase On 220V

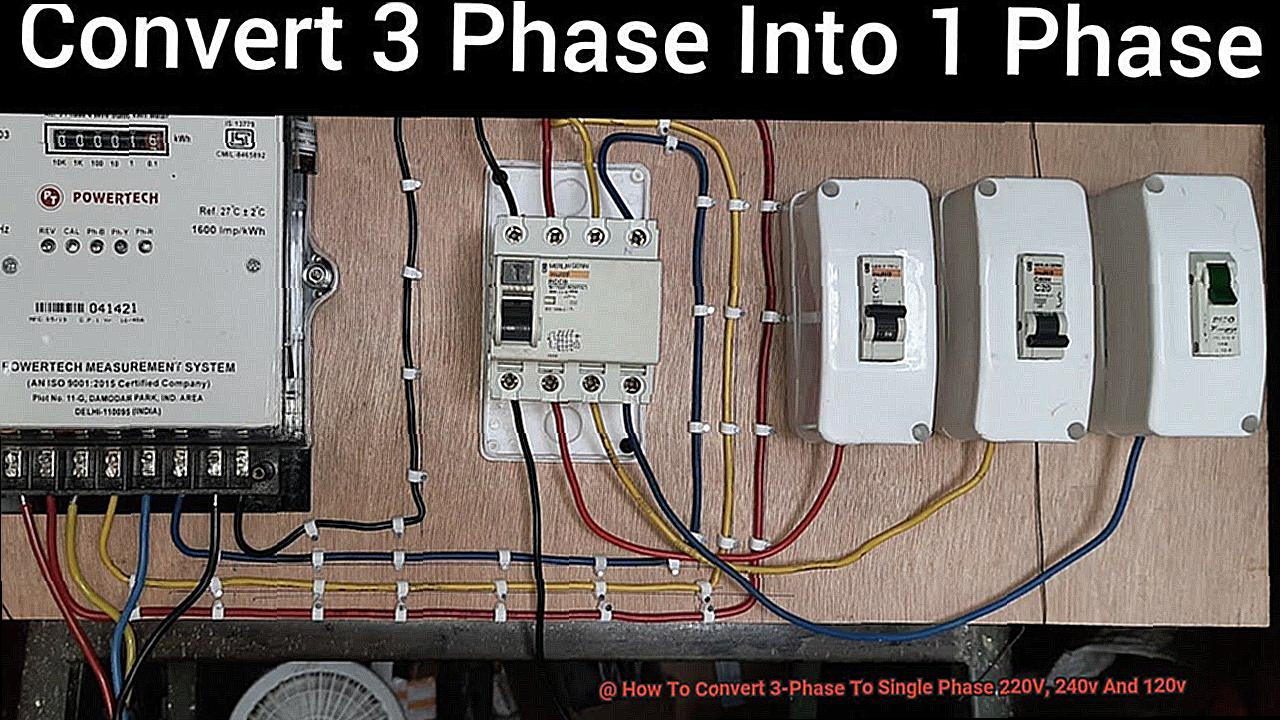
How To Convert 3 Phase 440 Volts Into Single 220 Volt Electrical
The Core Distinctions: Single-Phase Versus Three-Phase Power
Getting to Grips with the Basics
Before we embark on our conversion discussion, it’s really important to fully grasp what makes single-phase different from 3-phase power. Imagine electricity as a flowing river. In a single-phase system, you have one continuous flow. This is perfectly fine for most household gadgets—your toaster, your TV, your washing machine. The voltage varies, but it’s a consistent, if somewhat pulsating, delivery of power. This straightforwardness makes it economical to distribute and ideal for the relatively low power demands of homes and small businesses.
Three-phase power, by contrast, is like having three synchronized rivers, each reaching its peak at a different moment. When one river's flow is at its lowest, another is almost at its strongest, ensuring a much smoother, more constant delivery of power. This continuous and balanced power flow is incredibly beneficial for motors and other inductive loads. It leads to less vibration, greater efficiency, and more power output for a given size. This is why you'll find 3-phase power running everything from massive factory machinery to commercial air conditioning systems.
The phase difference, specifically 120 electrical degrees between each of the three phases, is the key to 3-phase power's superior performance for motors. This clever design allows 3-phase motors to start on their own and operate with remarkably consistent torque. Single-phase motors, on the other hand, often need extra windings or capacitors to create a rotating magnetic field, which can add complexity and reduce efficiency. This is a primary reason why a direct connection just won't work.
Furthermore, 3-phase power is significantly more efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances. To deliver a certain amount of power, 3-phase systems require less conductive material compared to single-phase systems. This means lower infrastructure costs and reduced energy loss, making it the preferred choice for industrial and heavy commercial applications where large amounts of power need to be distributed across a facility. Understanding these foundational differences is the groundwork upon which we can build our knowledge of successful 3-phase conversion.

Popular Conversion Methods: Rotary Phase Converters
Meet the Reliable Workhorse of Power Conversion
When it comes to transforming single-phase power into 3-phase, the **rotary phase converter** is often the first solution that comes to mind, and for good reason. It's a robust and dependable piece of equipment that has been a staple in workshops and small industrial settings for many years. Picture a clever device that takes your single-phase input and, through the ingenious action of a rotating motor-generator, spins up a third "synthetic" phase, thus creating a balanced 3-phase output. It's a mechanical marvel, in its own way, capable of powering a wide variety of 3-phase machinery.
A rotary phase converter essentially consists of a specially designed motor (the "idler" motor) that starts on single-phase power. Once it reaches its operating speed, it generates that crucial third phase. The output is a true 3-phase sine wave, which makes it suitable even for sensitive equipment. The quality of this output, especially its voltage balance, is extremely important for the efficient and long-term operation of your 3-phase motors. Higher quality converters will offer better voltage regulation, which is absolutely vital for protecting your valuable machinery.
One of the big advantages of rotary phase converters is their ability to handle various types of electrical loads, including resistive, inductive, and capacitive. This versatility makes them an excellent choice for workshops with multiple 3-phase machines, as they can power several pieces of equipment simultaneously, provided the converter is appropriately sized for the total connected load. Think of it as a central hub for all your 3-phase needs, transforming your single-phase supply into a powerful industrial asset.
However, it's worth noting that rotary phase converters do have their considerations. They consume a small amount of power even when not actively powering equipment, due to the continuous rotation of the idler motor. They also produce some audible noise, though modern designs have significantly reduced this. Proper sizing is absolutely essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity for both the converter and your connected equipment. Choosing a converter that's too small can lead to voltage imbalances and a shorter motor life, while an oversized one can be an unnecessary expense. It's all about finding that perfect balance!

Static Phase Converters: A Simpler Path
Discovering the Straightforwardness of Static Conversion
For those looking for a more compact and often more budget-friendly solution, the **static phase converter** offers an interesting alternative to its rotary counterpart. As its name suggests, a static converter doesn't have any moving parts. Instead, it uses capacitors and sometimes relays to create the third phase. It's more of a "set it and forget it" type of device, often preferred for applications where the 3-phase motor will be starting infrequently or where cost is a major consideration. Its simplicity is truly its greatest strength.
The way a static phase converter works is quite direct. When the 3-phase motor is started, the static converter uses capacitors to create a phase shift, essentially tricking the motor into starting on what it believes is 3-phase power. Once the motor is up and running, the converter's primary job is largely complete. It acts as a momentary boost, like giving a car a push-start, providing just enough power to get things moving. This characteristic makes it less ideal for applications requiring continuous, balanced 3-phase power for extended operation.
While static converters are more affordable and take up less space, they do come with certain limitations. They generally only provide a true 3-phase output during the motor's starting sequence. Once the motor is at full speed, the third phase generated by the converter might diminish or become significantly unbalanced. This can lead to reduced motor efficiency, higher operating temperatures, and potentially a shorter lifespan for the connected equipment, especially under heavy or continuous loads. It's a trade-off: convenience and lower initial cost versus consistent, sustained performance.
Static converters are best suited for situations where the 3-phase motor will be lightly loaded or used only occasionally. For example, a drill press or a small milling machine that isn't running constantly might work perfectly well with a static converter. However, for continuous-duty applications like a large air compressor or a heavy-duty lathe, the limitations of a static converter become more apparent. It's really important to carefully evaluate your specific needs and the demands of your equipment before choosing this simpler, yet less versatile, conversion method. Always consider the long-term health of your machinery!
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): The Modern Approach
Embracing the Digital Age of Power Management
In the evolving world of electrical engineering, **Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)**, also known as AC drives or inverters, have emerged as a remarkably sophisticated and adaptable solution for running 3-phase equipment on single-phase power. Unlike phase converters that just create a third phase, VFDs actually convert the incoming AC power to DC and then meticulously convert it back to a precisely controlled AC output. This digital prowess allows for unmatched control over the motor's speed, torque, and even direction, truly putting the power in your hands. It's like upgrading from a basic manual car to a sleek, electronically controlled automatic.
The fundamental principle behind a VFD's operation involves first converting the incoming single-phase AC voltage to a DC bus. This DC voltage is then "shaped" and synthesized into a new, variable frequency and variable voltage AC waveform using advanced electronics (typically IGBTs — Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors). This carefully crafted waveform, when applied to a 3-phase motor, creates smooth, controllable rotation. The ability to vary both frequency and voltage simultaneously is what gives VFDs their incredible flexibility and significant efficiency benefits.
One of the most compelling advantages of using a VFD for single-phase to 3-phase conversion is the extremely precise control it offers. You can adjust the motor's speed from almost zero to its full rated speed, which is incredibly valuable for applications needing fine-tuned operation, such as machine tools, pumps, and fans. Beyond speed control, VFDs also offer soft-start capabilities, which reduces mechanical stress on the motor and connected equipment, and significantly lowers inrush current, helping to prevent annoying circuit breaker trips. This level of control is simply not possible with traditional phase converters.
While VFDs typically have a higher upfront cost than static or even some rotary phase converters, their advantages in terms of energy efficiency, extending motor lifespan, and enhanced operational control often justify the investment, especially for critical or continuously operating machinery. They are also remarkably compact and quiet, making them ideal for situations where space is limited. However, proper selection and programming of the VFD are crucial, as they can be more complex to install and configure than simpler conversion methods. Consulting with an electrical professional is often recommended to ensure optimal performance and safety. It's a smart investment for the modern workshop!
How To Run 3phase Motor On Single PhaseRunning A 3 Phase
Important Considerations and Safety Advice
Making Sure Your Setup is Safe and Works Well
No matter which conversion method you choose, **safety and correct electrical practices are absolutely essential**. Working with electricity, especially at these voltage levels, carries inherent risks. Never underestimate the potential dangers. Always make sure that the work is performed by, or under the direct supervision of, a qualified electrician. Trying to install complex electrical systems without the necessary expertise can lead to serious injury, damage to your equipment, or even a fire. Your safety, and the safety of those around you, should always be the top priority.
Properly sizing your converter or VFD is incredibly important. An undersized unit will struggle to provide the necessary power, leading to drops in voltage, overheating, and early failure of both the converter and the motor it's connected to. On the flip side, an overly large unit might be an unnecessary financial burden. Always check the manufacturer's specifications for both your 3-phase equipment and the conversion device you've chosen. When in doubt, it's generally better to lean towards slightly oversizing, but precise calculations are key for the best performance and efficiency.
Ventilation is another aspect that's often overlooked but critically important. Converters, especially rotary types and VFDs, generate heat when they're running. Ensuring good airflow and proper cooling will prevent overheating, which can drastically shorten the life of the equipment and potentially lead to malfunctions. Place your converter or VFD in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight or excessive dust. Think of it as creating a comfortable working environment for your electrical components!
Finally, think about the quality of the power output. **Voltage balance** is a significant factor in how long and how efficiently 3-phase motors operate. Imbalanced voltages can cause motors to run hotter, draw too much current on one or more phases, and ultimately shorten their lifespan. High-quality rotary phase converters and VFDs offer much better voltage regulation. Regularly keeping an eye on your motor's performance and temperature can help you spot issues early, ensuring your valuable machinery continues to run smoothly and reliably for many years to come. Investing a little extra in a quality conversion solution will definitely pay off in the long run.
How To Convert 3Phase Single Phase 220V, 240v And 120v? The
Frequently Asked Questions
Your Common Questions Answered
Q1: Will running a 3-phase motor on a single-phase converter reduce its power output?
A1: This is a very common concern! While some very basic or incorrectly sized static phase converters might lead to a slight drop in power output or efficiency, especially under heavy loads, a properly sized rotary phase converter or a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) should allow your 3-phase motor to operate at or very close to its rated power. VFDs, in particular, often offer even better efficiency because they can precisely control motor speed and torque. It really boils down to picking the right tool for the task and making sure it's well-matched to what your equipment needs.
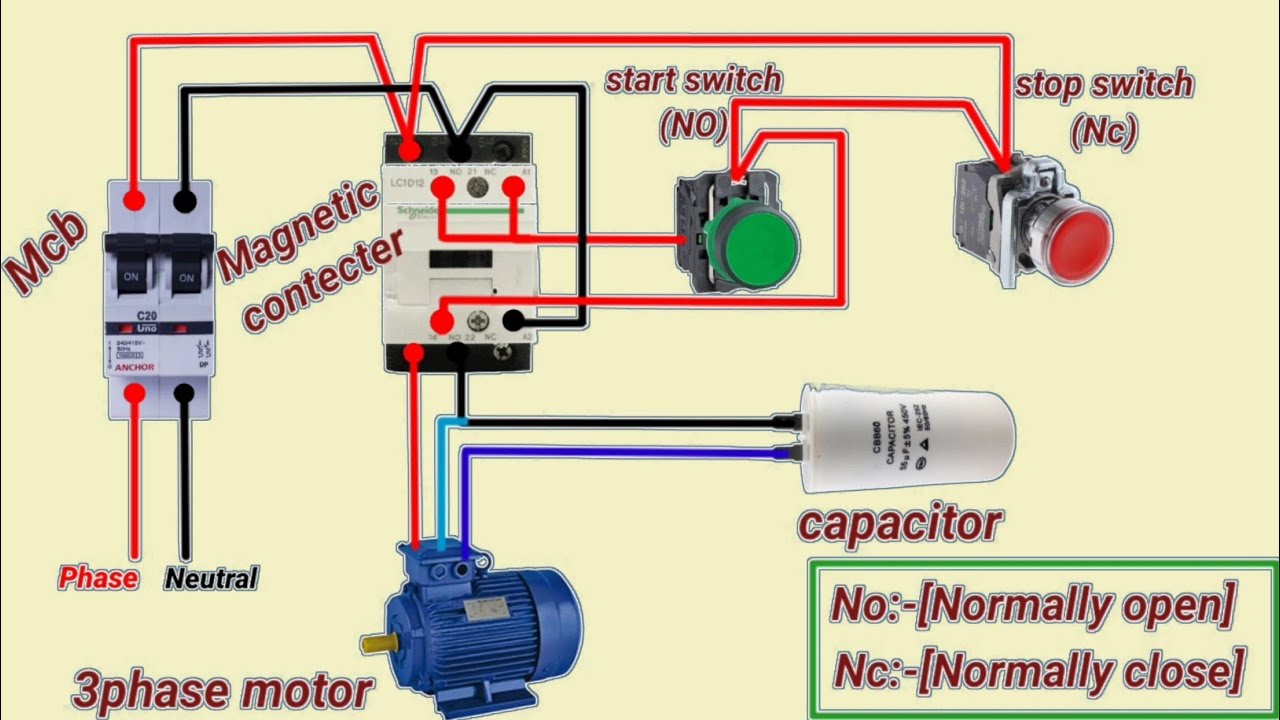
Q2: Can I simply wire a 3-phase motor to two terminals of my 220V single-phase supply?
A2: Absolutely not! Please, for the sake of your equipment and your personal safety, do not attempt this. Three-phase motors need three distinct phases with a specific phase relationship (120 degrees apart) to create the rotating magnetic field necessary for proper operation. Connecting it to just two terminals of a single-phase supply will, at best, cause the motor to hum loudly and fail to start, and at worst, lead to severe damage to the motor windings, tripping circuit breakers, or even an electrical fire. This is why dedicated conversion methods are essential, not just an optional extra.
Q3: How do I figure out the right size of phase converter or VFD for my equipment?
A3: Sizing is critical! For most situations, you'll need to know the **full load amperage (FLA)** of your 3-phase motor, which is usually found on its nameplate. For rotary phase converters, a good general guideline is to size the converter at 2 to 3 times the FLA of the largest motor, or the total FLA if you're running multiple motors at the same time. For VFDs, you typically match the VFD's rated current to the motor's FLA. However, specific motor characteristics (like high starting current for compressors) and the type of load (constant torque vs. variable torque) can influence the sizing. Always consult the manufacturer's instructions for both your motor and the conversion device, and when in doubt, definitely talk to a qualified electrician. Getting it right ensures both efficiency and a long life for your equipment!